Unleashing Peak Performance: How Human Relations, Work Discipline, and Work Ethic Drive Employee Success
Keywords:
human relations, work discipline, work ethic, employee performanceAbstract
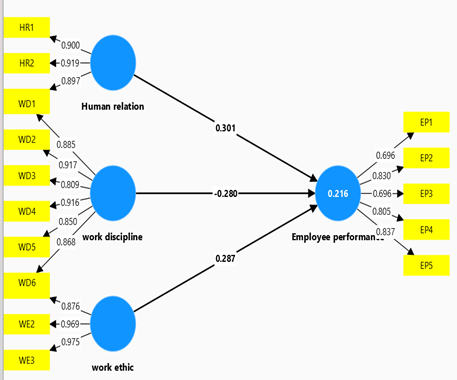
This study examines the influence of human relations, work discipline, and work ethic on employee performance. Using a quantitative approach with a survey research design, data were collected from 250 employees in the manufacturing industry through a validated questionnaire. Data analysis was conducted using SEM-PLS to test the research hypotheses. The results indicate that human relations and work ethic significantly improve employee performance, with each variable positively influencing and supporting the proposed hypothesis. However, work discipline contributes significantly negatively. Specifically, good human relations facilitate collaboration and motivation, work discipline decreases efficiency and consistency, and work ethic encourages commitment and dedication to tasks. These findings underscore the importance of managing interpersonal relationships, reviewing to reduce disciplinary strictness, and strengthening the work ethic in achieving employee success. The practical implication of this study is the urgent need for organizations to develop training programs and work cultures that support these three aspects to optimize employee performance.References
Akdere, M., & Egan, T. (2020). Transformational leadership and human resource development: Linking employee learning, job satisfaction, and organizational performance. Human Resource Development Quarterly, 31(4), 393–421. https://doi.org/10.1002/hrdq.21404
Akgunduz, Y., & Gürel, D. A. (2019). Role stress and turnover intention in hotels: The mediating role of organizational enthusiasm and unstimulating work. Tourism, 67(3), 222–238.
Algoe, S. B. (2019). Positive Interpersonal Processes. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 28(2), 183–188. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721419827272
Alshwayat, D., MacVaugh, J. A., & Akbar, H. (2020). A Multi-level Perspective on Trust, Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing Cultures in a Highly Formalized Organization. Journal of Knowledge Management, 25(9), 2220–2244.
Bob-Manuel, I. V., Georgewill, I. A., & Tamunomiebi, M. D. (2024). Self-awareness and Workplace Harmony of Printing Companies in Port Harcourt, Nigeria. International Journal of Innovative Psychology & Social Development, 12(4), 40–50. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13923234
Bugdol, M. (2018). A Different Approach to Work Discipline. In A Different Approach to Work Discipline. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74008-9
Cherian, J., Gaikar, V., Paul, R., & Pech, R. (2021). Corporate culture and its impact on employees’ attitude, performance, productivity, and behavior: An investigative analysis from selected organizations of the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 7(1), 1–28. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc7010045
Ernest, A. (2021). Discipline and Achievement of Organizational Objectives. International Journal of Institutional Leadership, Policy and Management, 3(3), 471–489. www.ijilpm.com.ng
Grabowski, D., Chudzicka-Czupała, A., & Stapor, K. (2021). Relationships between work ethic and motivation to work from the point of view of the self-determination theory. PLoS ONE, 16(7 July), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0253145
Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2022). A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) Third Edition. In Women Entrepreneurs. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781032725581-7
Konadu, K., Opoku Mensah, A., Koomson, S., Abraham, E. M., Amuzu, J., & Agyapong, J. A. M. (2023). A model for improving the relationship between integrity and work performance. International Journal of Ethics and Systems, April 2024. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOES-01-2023-0017
Mesdaghinia, S., Rawat, A., & Nadavulakere, S. (2019). Why Moral Followers Quit: Examining the Role of Leader Bottom-Line Mentality and Unethical Pro-Leader Behavior. Journal of Business Ethics, 159(2), 491–505. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-018-3812-7
Nabhan, F., & Munajat, M. (2023). The role of work engagement and organizational commitment in improving job performance. Cogent Business and Management, 10(2). https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2023.2235819
Pisriwati, S. A., Hardi, Y., & Siswanto, D. H. (2024). Enhancing Organizational Development through Principal Leadership to Improve Teacher and Staff Work Discipline. Journal of Organizational and Human Resource Development Strategies, 1(01), 52–62. https://doi.org/10.56741/ohds.v1i01.670
Potnuru, R. K. G., & Sahoo, C. K. (2016). HRD interventions, employee competencies and organizational effectiveness: an empirical study. European Journal of Training and Development, 40(5), 345–365. https://doi.org/10.1108/EJTD-02-2016-0008
Puspitasari, T. W., Akbar, M. A., & Lina, R. (2025). Leadership Style and Work Discipline on employee performance. Advances in Human Resource Management Research, 3(1), 15–29. https://doi.org/10.60079/ahrmr.v3i1.321
Ramlawati, Serang, S., Arminas, J., & Wicaksono, R. (2023). The role of ethical leadership on employee commitment to the organization: The mediating role of job satisfaction and job engagement. Organizatsionnaya Psikhologiya, 13(1), 73–91. https://doi.org/10.17323/2312-5942-2023-13-1-73-91
Steg, L. (2016). Values, Norms, and Intrinsic Motivation to Act Proenvironmentally. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 41, 277–292. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-environ-110615-085947
Sumarmi, S., Tjahjono, H. K., Qamari, I. N., & Shaikh, M. (2024). Authentic Leadership and Team Performance: Exploring the Mediating Role of Dynamic Adaptive Capability. Journal of Leadership in Organizations, 6(2), 159–180. https://doi.org/10.22146/jlo.94502
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Conference Proceedings Volume
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Saptaningsih Sumarmi, Samsudin, Andri

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.











